Understanding Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs): Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that spread through sexual contact. These infections can affect individuals of all ages, genders, and sexual orientations. Understanding STDs, including their symptoms, prevention methods, and available treatments, is crucial for promoting sexual health and well-being. In this article, we’ll explore the various aspects of STDs to provide comprehensive insights into this important topic.
What Are STDs?
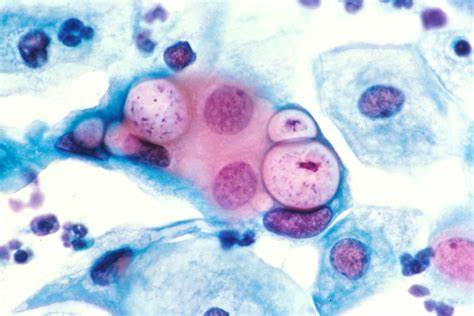
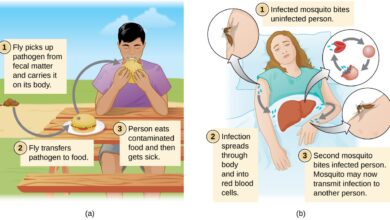
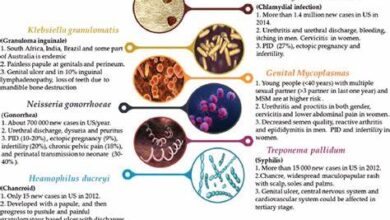
Sexually transmitted diseases, also known as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites that are transmitted through sexual activity. This includes vaginal, anal, or oral sex, as well as genital touching. STDs can be passed from one person to another through the exchange of bodily fluids, such as blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and saliva. Common STDs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, genital herpes, HIV/AIDS, and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Symptoms of STDs
STDs can manifest with a wide range of symptoms, which may vary depending on the type of infection and individual factors. Some STDs may cause noticeable symptoms, while others can be asymptomatic, meaning they show no outward signs. Common symptoms of STDs include:
- Genital sores or ulcers
- Pain or burning during urination
- Unusual discharge from the penis or vagina
- Itching, irritation, or inflammation in the genital area
- Painful intercourse
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Flu-like symptoms, such as fever and fatigue
Prevention of STDs
Preventing STDs involves adopting healthy sexual practices and taking proactive measures to reduce the risk of infection. Here are some key prevention strategies:
1. Practice Safe Sex
Using condoms consistently and correctly during sexual activity can significantly reduce the risk of contracting STDs. Condoms act as a barrier that prevents the exchange of bodily fluids, thereby reducing the likelihood of transmission.
2. Limit Sexual Partners
Limiting the number of sexual partners and engaging in monogamous relationships can reduce the risk of exposure to STDs. Knowing the sexual history of your partner(s) and discussing STD testing can also help minimize risk.
3. Get Vaccinated
Vaccines are available for certain STDs, such as HPV and hepatitis B. Getting vaccinated can provide protection against these infections and lower the risk of transmission.
4. Practice Mutual Monogamy
Mutual monogamy, where both partners agree to be sexually exclusive with each other, can help prevent the spread of STDs. Regular communication and honesty about sexual health are essential in maintaining a mutually monogamous relationship.
5. Get Tested Regularly
Regular STD testing is crucial for early detection and treatment. Many STDs can be asymptomatic, so getting tested even in the absence of symptoms is important, especially for individuals who are sexually active or have multiple partners.
Treatment of STDs
Treatment for STDs varies depending on the type of infection and its severity. It typically involves the use of antibiotics for bacterial infections or antiviral medications for viral infections. In some cases, STDs may require long-term management or ongoing treatment to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmission. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential for managing STDs effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding sexually transmitted diseases is essential for promoting sexual health and reducing the spread of infections. By educating ourselves and others about the symptoms, prevention methods, and available treatments for STDs, we can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their sexual health. Practicing safe sex, getting vaccinated, and getting tested regularly are important steps in preventing and managing STDs. Together, we can work towards creating a safer and healthier environment for everyone.