The Role of Education in Combating STDs: Empowering Communities for Safer Practices
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) continue to be a significant public health concern worldwide, with millions of new cases reported annually. While medical advancements have provided treatments and preventive measures, the key to effectively combating STDs lies in education and community empowerment. This article explores the pivotal role of education in promoting safer practices and reducing the prevalence of STDs within communities.
Understanding STDs
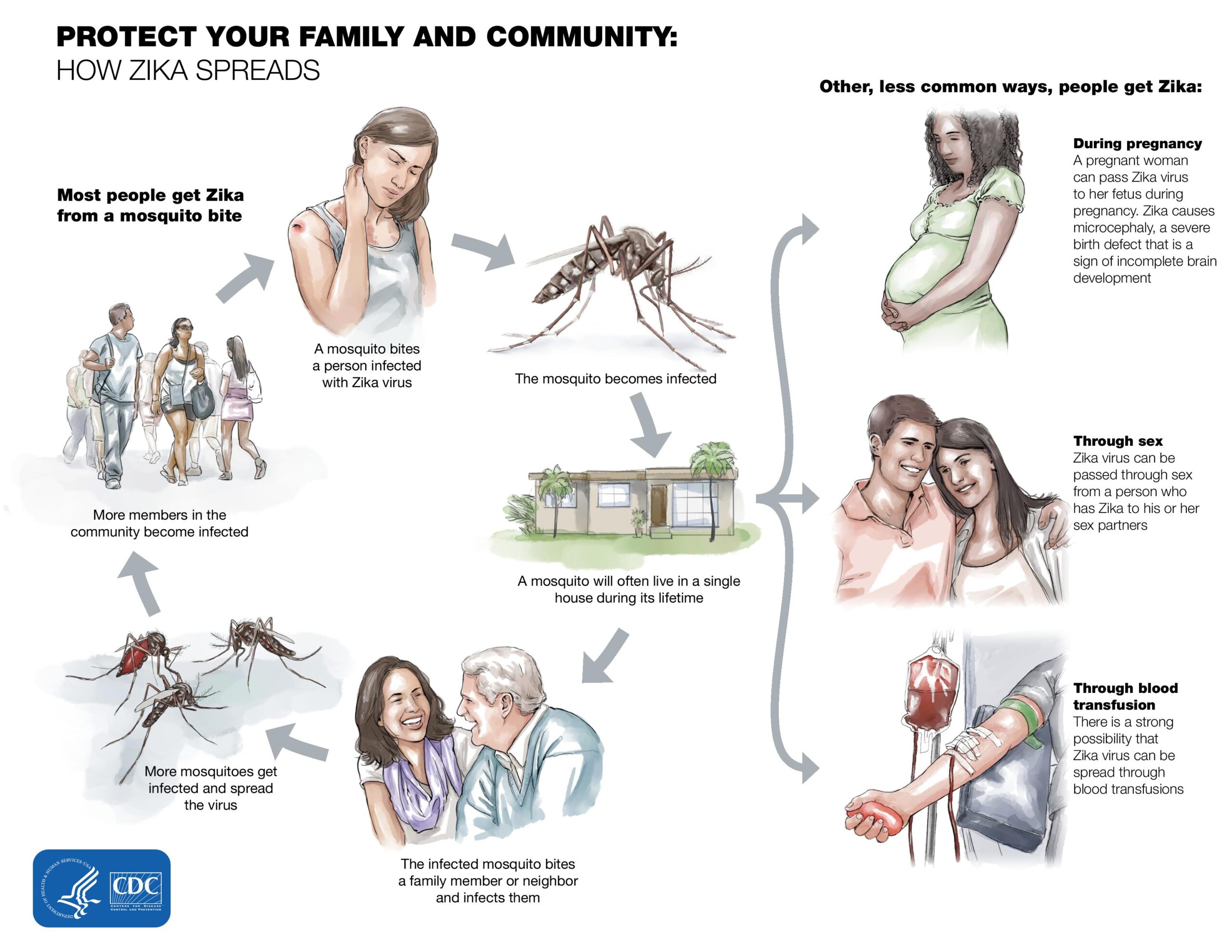
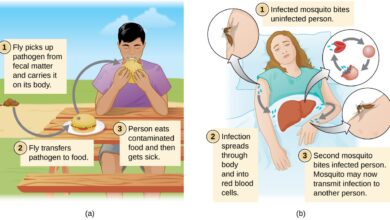
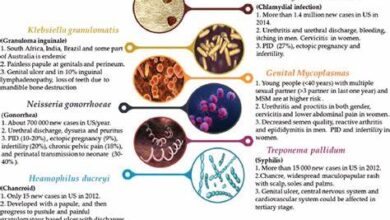
Before delving into the role of education, it’s essential to understand what STDs are and how they spread. STDs are infections that are primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Common STDs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, herpes, HIV/AIDS, and HPV. Each STD has its own set of symptoms, transmission methods, and potential health complications.
The Importance of Education
Education plays a crucial role in combating STDs by raising awareness, promoting prevention strategies, and reducing stigma. Comprehensive sexual education programs provide individuals with accurate information about STDs, including how they are transmitted, common symptoms, and available treatments. By educating communities about the risks associated with unprotected sex and the importance of regular testing, individuals are empowered to make informed decisions about their sexual health.
Breaking the Stigma
One of the significant barriers to addressing STDs is the stigma and shame often associated with these infections. Education serves as a powerful tool in breaking down these barriers by fostering open and honest conversations about sexual health. By promoting a non-judgmental and inclusive approach to discussing STDs, education helps individuals feel more comfortable seeking testing, treatment, and support.
Promoting Safer Practices
Education empowers individuals to adopt safer sexual practices that can reduce the risk of contracting STDs. This includes promoting the use of condoms, practicing mutual monogamy, and discussing sexual histories with partners. Additionally, education encourages regular STD testing, which allows for early detection and treatment of infections, ultimately reducing transmission rates within communities.
Targeting Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations, such as adolescents, LGBTQ+ individuals, and marginalized communities, may face increased risks of STD transmission due to various social and economic factors. Education programs should be tailored to address the specific needs and challenges of these populations, providing culturally sensitive information and resources to promote safer practices and access to healthcare services.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a critical role in educating patients about STDs and providing essential services such as testing, treatment, and counseling. By incorporating STD screening into routine healthcare visits and offering comprehensive sexual health assessments, providers can identify infections early and offer appropriate interventions. Education and training for healthcare professionals are essential to ensure that they have the knowledge and skills necessary to address STDs effectively.
Community Engagement and Outreach
Education initiatives should involve community engagement and outreach efforts to reach individuals where they are. This may include hosting workshops, distributing educational materials, and partnering with local organizations and schools. By actively engaging with communities, education programs can increase awareness, reduce stigma, and promote healthier behaviors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, education plays a vital role in combating STDs by empowering communities with knowledge, promoting safer practices, and reducing stigma. By investing in comprehensive sexual education programs, targeted outreach efforts, and healthcare provider training, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of STDs and improving the overall sexual health and well-being of individuals and communities worldwide.