Diagnosis and Treatment of STDs: Available Tests and Therapies
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) continue to be a significant public health concern worldwide. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial in managing these infections and preventing their spread. In this article, we will explore the various diagnostic tests and treatment options available for STDs.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of STDs is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it allows for prompt treatment, which can prevent complications such as infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and certain cancers associated with some STDs. Secondly, it helps in preventing further transmission of the infection to sexual partners. Lastly, early diagnosis reduces the risk of long-term health consequences and improves overall prognosis.
Diagnostic Tests
1. Blood Tests
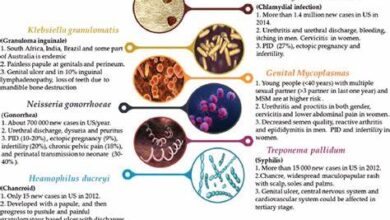
Blood tests are commonly used to diagnose STDs such as HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis. These tests detect the presence of antibodies or antigens produced by the body in response to the infection. For example, the HIV antibody test detects antibodies produced by the immune system in response to HIV infection, while the syphilis test detects antibodies against the bacterium Treponema pallidum.
2. Urine Tests
Urine tests are convenient and non-invasive diagnostic tools used to detect STDs such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. These tests can identify the presence of bacteria in the urine sample, indicating an active infection. Urine tests are particularly useful for individuals who may feel uncomfortable or hesitant to undergo genital examinations.
3. Swab Tests
Swab tests involve collecting samples from the genital area, throat, or rectum using a cotton swab. These samples are then analyzed in a laboratory to detect the presence of bacteria or viruses. Swab tests are commonly used to diagnose STDs such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, and human papillomavirus (HPV).
4. Physical Examinations
In some cases, healthcare providers may perform physical examinations to diagnose STDs. During the examination, the healthcare provider may inspect the genital area for any signs of infection, such as sores, lesions, or unusual discharge. Physical examinations are often complemented by other diagnostic tests for a comprehensive evaluation.
Treatment Options
1. Antibiotics
Many bacterial STDs, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis, can be effectively treated with antibiotics. These medications work by killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria responsible for the infection. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the healthcare provider to ensure the infection is completely eradicated.
2. Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications are used to treat viral STDs such as herpes, HIV, and hepatitis. These medications work by inhibiting the replication of the virus within the body. While antiviral drugs cannot cure viral STDs, they can help manage symptoms, reduce the frequency of outbreaks, and slow the progression of the disease.
3. Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)
ART is a combination of medications used to treat HIV infection. This therapy involves taking a combination of antiretroviral drugs daily to suppress the replication of the virus and preserve immune function. ART can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with HIV and reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to others.
4. Topical Treatments
Some STDs, such as genital warts caused by HPV infection, can be treated with topical medications applied directly to the affected area. These treatments work by destroying the warts or stimulating the immune system to eliminate the virus. However, topical treatments may require multiple applications over several weeks to achieve optimal results.
Conclusion
Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential in managing sexually transmitted diseases and preventing their complications. A variety of diagnostic tests are available to detect STDs, including blood tests, urine tests, swab tests, and physical examinations. Treatment options vary depending on the type of infection and may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, antiretroviral therapy, and topical treatments. It is essential for individuals to seek medical attention if they suspect they may have been exposed to an STD to receive timely diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, practicing safe sex, including the consistent and correct use of condoms, and undergoing regular STD testing are essential components of maintaining sexual health and preventing the spread of infections.