Emerging Trends: Addressing the Rise of STD Cases in Modern Society
In recent years, the global healthcare landscape has witnessed a concerning surge in the prevalence of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs). Despite advancements in medical science and increased awareness campaigns, the incidence of STDs continues to rise, posing significant challenges to public health systems worldwide. This article explores the emerging trends contributing to the escalation of STD cases in modern society and suggests strategies to address this pressing issue.
Factors Fueling the Rise of STD Cases
1. Changes in Sexual Behavior
The evolution of societal norms and attitudes towards sex has led to shifts in sexual behavior patterns. Increased casual and unprotected sexual encounters, coupled with changing relationship dynamics, contribute to the spread of STDs.
2. Lack of Comprehensive Sex Education
Inadequate sex education programs in schools and communities fail to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to make informed decisions about their sexual health. Misinformation and misconceptions about STDs perpetuate risky behaviors and hinder preventive measures.
3. Stigma and Discrimination
The persistent stigma surrounding STDs discourages individuals from seeking testing, treatment, and support services. Fear of judgment and discrimination prevents open dialogue about sexual health issues, further perpetuating the spread of infections.
4. Limited Access to Healthcare Services
Unequal access to healthcare services, particularly among marginalized populations, exacerbates the burden of STDs. Economic barriers, geographical disparities, and cultural factors contribute to limited testing, diagnosis, and treatment options for affected individuals.
Commonly Reported STDs
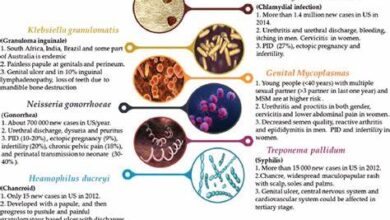
1. Chlamydia
Chlamydia remains one of the most prevalent STDs globally, with a significant number of cases reported each year. Often asymptomatic, untreated chlamydia infections can lead to severe complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility.
2. Gonorrhea
The emergence of drug-resistant strains of gonorrhea poses a growing threat to public health. Inadequate treatment regimens and over-reliance on antibiotics contribute to the development of resistance, challenging efforts to control the spread of the disease.
3. Syphilis
Despite being easily treatable with antibiotics, syphilis cases have been on the rise in recent years. The resurgence of syphilis outbreaks highlights the importance of early detection and prompt treatment to prevent long-term complications.
4. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
While significant progress has been made in the prevention and treatment of HIV, the virus continues to affect millions of people worldwide. Stigma, discrimination, and barriers to accessing antiretroviral therapy remain formidable challenges in the fight against HIV/AIDS.
Addressing the Epidemic: Strategies for Prevention and Control
1. Comprehensive Sex Education
Implementing evidence-based sex education programs in schools and communities is essential to promote healthy behaviors, improve sexual literacy, and reduce the risk of STD transmission.
2. Increased Access to Testing and Treatment
Expanding access to affordable and confidential testing services, as well as timely treatment and counseling, is crucial to ensure early detection and management of STDs.
3. Destigmatization and Advocacy
Combatting stigma and discrimination surrounding STDs requires concerted efforts from healthcare providers, policymakers, and advocacy groups to promote acceptance, empathy, and support for affected individuals.
4. Embracing Technology and Innovation
Harnessing the power of technology, including telemedicine, mobile health applications, and online platforms, can enhance outreach, education, and access to sexual health services, particularly among underserved populations.
5. Community Engagement and Collaboration
Fostering partnerships between healthcare providers, community organizations, and government agencies is essential to develop targeted interventions, raise awareness, and mobilize resources to combat the spread of STDs.
Conclusion
The escalating prevalence of STDs poses a significant public health challenge in modern society. Addressing this epidemic requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses comprehensive sex education, increased access to testing and treatment, destigmatization efforts, technological innovations, and community collaboration. By prioritizing prevention, early detection, and supportive interventions, we can work towards reducing the burden of STDs and promoting healthier outcomes for individuals and communities worldwide.